How to CALCULATE numbers for IRS taxes: pen and paper, spreadsheets, software
Evolving blog post - photos coming someday!
This is step three of the Prep for IRS Tax process. To see all the steps, click here.
In a nutshell
You need to report some numbers related to your business AND have some evidence to back them up (receipts, bank statements, etc.). How you add up the numbers is up to you!
The numbers (eventually) get reported on the Schedule C. If you use software or a tax preparer, they will ask you questions, then put those numbers onto the Schedule C for you.
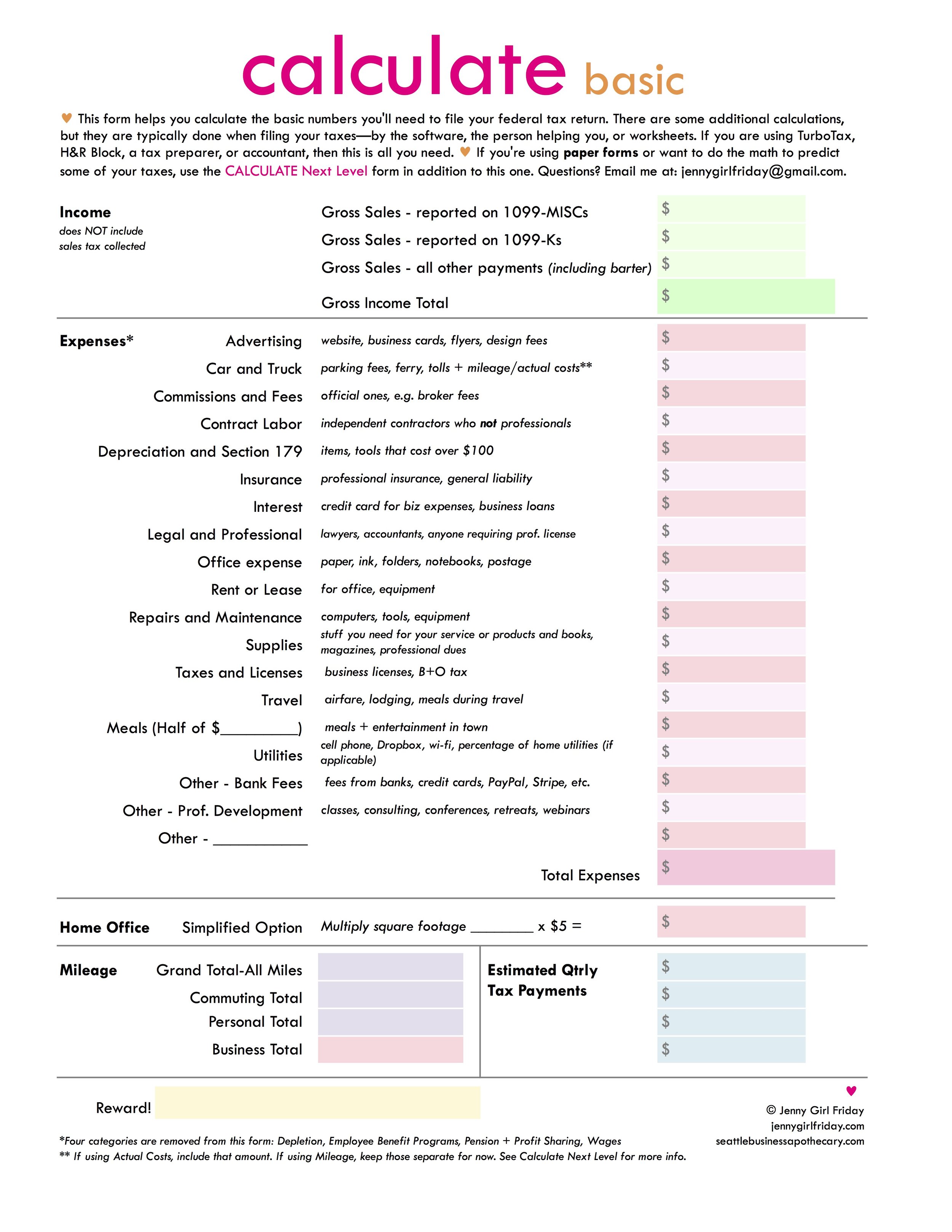
Consider using the handy worksheets below to keep track of your numbers.
Alert: This blog post may look really complicated, and I apologize for that! It's tough because every situation is different, and I'm attempting to speak to a variety of situations in one post. ♥ Please know: once you get into the material, it usually starts to make sense. Also, I invite you to email me with any questions! jennygirlfriday@gmail.com
ProTip: Print the Calculate-Basic worksheet, and just start filling in what you know. Then come back to the post for more ideas when needed.
ProTip: Get a friend to help you with this. They can read the instructions, then together, you can figure out how to proceed.
The Calculate-Basic includes everything you need for MOST situations. The Calculate-Next Level is helpful if you're planning to file using paper forms, or if you want to predict your self-employment tax amount.
Gross Sales
AKA Gross Income / Total Deposits
Important: This number NEVER includes any sales tax collected.
You need to have a total Gross Sales number, and a record to back this up. Perhaps you already have this total, or parts of it.......or perhaps you have to create it still. Here are some options.
Different Ways to Keep / Create a Gross Sales Record
If you already have this record, great! If you need to make one up for last year, read on! The basic process is:
1 Find the payment amounts
2 Make a Record
3 Find the Total
4 Format for the IRS
1 - Find the payment amounts
Here are all the places to look:
- Bank Statements - look at deposit records
- Deposit Slips
- Copies of Receipts/Invoices
- Reports from Commerce sites
- Calendar - find all appointments and mark what you got paid for each
2 - Make a Record
Ideally, include the date, purchaser name, and amount of each.
These are options for you to choose from:
- Keep a list of all payments in a notebook
- Record payments in a spreadsheet
- Print out all summary reports from websites you use, keep as your records
- Use software or an app (such as Quickbooks or Fresh Books)
3 - Find the Total
Add up all your numbers to find your Total Payments by customers. This is your Gross Sales.
Do NOT include any sales tax collected.
- Use calculator
- Put into a spreadsheet, and use formulas to add
- If using software, go to the Reports section to get the totals
4 - Format for the IRS
Did you get any 1099-MISCs or 1099-Ks for your business? These are simply proofs of payments that someone else made to your business. The numbers on these forms should already be included in your Gross Sales amount.
> If you're filing with Paper Forms, then you just report your Gross Sales, which includes the totals on these forms. You do NOT need to list out their amounts separately.
> If you're filing with software or an accountant, they will ask you for your Gross Sales in parts. So you'll need to find the subtotals for:
___1099-MISCs
___1099-Ks
___ All other payments (including barter)
___ Total of Gross Sales
Expenses
Okay, options! Here are three of my favorite. There are more options and variations. Hopefully this will give you an overall idea, and you can create something that works for you.
Note: For evidence of our business expenses, receipts from the purchase are best. The IRS will also accept bank and credit card statements.
Pen and Paper
With Receipts
1. Look at the categories of business expenses (on the Calculate-Basic sheet or the Schedule C)
2. Make piles with your receipts in each category.
3. Add up the totals for each, and fill in the chart. Perhaps write these amounts on pieces of paper to keep track, one for each category.
4. Suggested: staple each stack of receipts together.
With Bank Statements
1. Look at the categories of business expenses (on the Calculate-Basic sheet or the Schedule C)
2. Get a piece of paper for each category, label at the top.
3. Go through Bank Statements. Find each business expense. Highlight, circle, or underline it on the statement.
4. Decide which category the expense falls in. Write each expense on the corresponding piece of paper. (For example, if you see a line for "Office Max", write the amount on the paper that labeled "Office Expense".)
5. When all expenses have been recorded, add up to get the totals. Record on the Calculate-Basic worksheet by category.
Spreadsheet
1. Look at the categories of business expenses (on the Calculate-Basic sheet or the Schedule C)
2. Label a column or separate tab with each category. (Depending on how you like to work.)
3. Go through your receipts and Bank Statements. Find each business expense. Highlight, circle, or underline on the statement.
4. Decide which category the expense falls in. Add it to the column or the tab.
5. When all have been recorded, add up to get the totals. Record on the Calculate-Basic worksheet.
Quickbooks or Other Software
1. Finish inputing/uploading all expenses for 2017
2. Find the Reports page
3. Select Profit and Loss statement
4. For the time period, select Last Year
5. Look at the report. Review each category.
6. Make any adjustments.
7. Print the Profit and Loss statement. Or, record the amounts on the Calculate-Basic sheet.
Special Expenses
These get calculated in special ways, so deserve their own section.
Special Expense - Mileage
There are two ways to deduct driving expenses. For each vehicle, choose one method and stick to it each year.
Option A: Actual expense. (Less common)
With this option, you collect and report ALL costs associated with your vehicle: gas, insurance, repairs, maintenance, and tab renewals. If you use it part for personal and part for business, you need to calculate what percentage is used for business. Then take that percentage of the total costs.
So, if you use for business 30% of the time, you'd deduct 30% of all costs associated with that vehicle.
Add this expense to the Car and Truck Category.
Option B: Mileage Deduction (most common)
For every mile that you drive for business, you get to deduct a specified amount. In 2017 it was 53.5 cents per mile. With this method, you need to know your total business miles. Additionally, you're required to have a record. The easiest way is to use an app, such as MileIQ. Or, you can keep a log book.
For most forms of filing, you'll be asked for:
___ Starting Odometer reading, on January 1
___ Ending Odometer reading, on December 31
___ Grand Total of All Miles
___ Total of Personal Miles
___ Total of all Commuting Miles (driving to and from an office)
___ Total of all Business Miles
To Claim the Expense:
If using Paper Forms
A. Calculate Total Business Miles x 0.535 =____________.
B. Add this to your Car and Truck Total
If using Software or Working with a Tax Pro
A. Have all of your Mileage Totals Handy
B. Do NOT include in Car and Truck expense
C. Provide information when asked, and they will calculate and deduct
Special Expense - Home Office
If you have a home office that meets certain requirements, then you can make a deduction. There's a Regular Method (that's complicated) to do this, and a Simplified Method. I will only speak to the Simplified Method. To learn more, go to IRS.gov, or ask your accountant.
A. Decide if you meet the requirements: the space is ONLY used for business, and it is your principle work space.
B. Measure the Square Footage.
C. Multiply Square Footage by $5=_____________
D. If using Paper Forms, claim this expense on the Schedule C on Line 30. (It is in a separate place than other expenses.) Also, consider researching or asking someone about Schedule A. I have yet to learn about this.
E. If using software or working with a tax pro, input when prompted.
♥ If this is your first year..........hang in there........and just try your best! If you find out in the future that you did something wrong, or forgot some major deductions, don't worry, you can amend tax returns from previous years.
Actually, that goes for everybody. Just try your best. Take things one step at a time. Do what you can. Reach out for help: from a friend or colleague, email me, meet with a tax volunteer at the library, or your bookkeeper or accountant.
To read about options for Filing, click here.
For the next Tax Help Pop-up Shop, click here.
: ) Jenny Girl Friday
P.S. Know any other self-employed Seattleites who could use this information? Please forward freely!
P.S.2 Are you already signed up for Sidekick Services? If not, click here and join the list to receive tax + license reminders, how-tos, inspiration and more delivered to your inbox.